7.8. Form Elements
In a form model, an input field is typically paired with the text label (<label> and <input> tags are
used together). Such a pair is also called a form model's element.
Analogous to an HTML form field, a form model's element may contain the name and other (optional) attributes (e.g. "id", "class", etc.) Additionally, you may set options to an element; the options mostly allow you to specify the text and attributes for the element's label.
All form model's elements are inherited from the base class Element which also belongs
to the Zend\Form component. The Element base class implements the ElementInterface interface.
The class inheritance diagram is shown in figure 7.11.
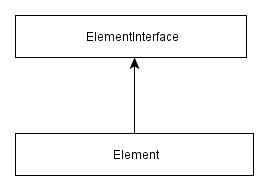 Figure 7.11. Form element class inheritance
Figure 7.11. Form element class inheritance
Concrete form element classes extend the Element base class. They are listed in tables 7.3 - 7.7.
These classes live in the Zend\Form\Element namespace.
| Class name | Description |
|---|---|
Button |
Button. |
Checkbox |
Check box. |
File |
File field. |
Hidden |
Hidden field. |
Image |
Image field. |
Password |
Password field. |
Radio |
Radio button. |
Select |
Dropdown list. |
Submit |
Submit button. |
Text |
General-purpose text input field. |
Textarea |
Multi-line text area. |
| Class name | Description |
|---|---|
Color |
Color picker. |
Date |
Date picker. |
DateTime |
Date & time (with time zone). |
DateTimeLocal |
Date & time (without time zone). |
Email |
E-mail field. |
Month |
Month input field. |
Number |
A text input field accepting numbers. |
Time |
Text input field for entering time. |
Url |
Text input field for entering an URL. |
Week |
Text input field for entering days of week. |
Range |
Range field (slider). |
| Class name | Description |
|---|---|
MultiCheckbox |
A group of related check boxes. |
DateTimeSelect |
Date & time select. |
DateSelect |
Date select. |
MonthSelect |
Month select. |
| Class name | Description |
|---|---|
Captcha |
Human check image. |
Csrf |
Cross-site request forgery prevention. |
| Class name | Description |
|---|---|
Collection |
Element collection. |
In the tables above, you can see that the ZF3-provided form elements have direct mapping on HTML4 and HTML5 input fields (discussed in the beginning of this chapter).
For your convenience, ZF3 also provides several "compound" fields. The
MultiCheckbox field is a field which is composed of a group of typical checkboxes related to
each other. The DateTimeSelect, DateSelect, and MonthSelect elements are analogous to corresponding
HTML5 elements, but simulate them with the usual select fields. These input fields have an advantage in that they
are supported by all web browsers, unlike the corresponding HTML5 fields. The visual representation of
these elements can be seen in figure 7.12.
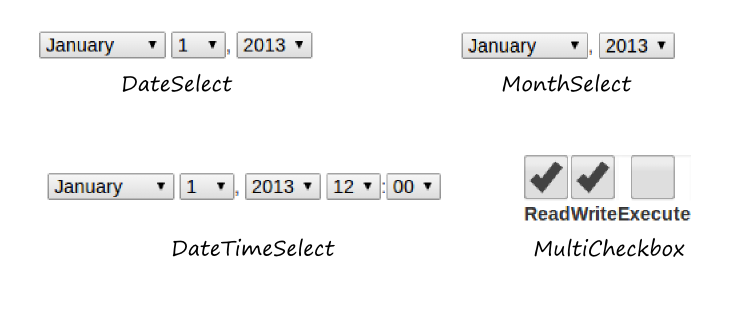 Figure 7.12. Compound form fields
Figure 7.12. Compound form fields
Additionally, ZF3 provides "security" form fields Captcha and Csrf which
can be used on a form for enhancing the security. The Captcha element is a graphical element (image)
that is placed on a form for checking if the site user is a human or a robot. The Csrf element has
no visual representation and is used for
prevention of hacker attacks related to cross-site request forgery 20.
20) Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is a type of malicious exploit of a website whereby unauthorized commands are transmitted from a user that the website trusts.
There is another special form element called Collection. This element is analogous to fieldset,
because it allows you to group related form elements. But, it is designed for adding form elements dynamically by binding
an array of objects to the form.
7.8.1. Adding Elements to a Form Model
The methods inherited by the Form base class from the Fieldset class are used to
add elements (and fieldsets) to the form model. These methods are summarized in the table 7.8.
| Method name | Description |
|---|---|
add($elementOrFieldset, $flags) |
Attaches an element (or fieldset). |
has($elementOrFieldset) |
Checks whether certain element is attached. |
get($elementOrFieldset) |
Retrieves the given element (or fieldset) by name. |
getElements() |
Retrieves all attached elements. |
getFieldsets() |
Retrieves all attached fieldsets. |
count() |
Return the count of attached elements/fieldsets. |
remove($elementOrFieldset) |
Removes the element (or fieldset). |
Particularly, we are interested in the add() method which is used to attach
an element to a form. The add() method takes two arguments: the first one (named $elementOrFieldset)
is an element to insert, and the second one (named $flags) is the optional flags.
The $elementOrFieldset parameter may either be an instance of an
Element-derived class (or the Fieldset class), or an array describing the element that
should be created.
The optional $flags argument is an array which may contain a combination of the following keys: name
(allows you to set the element's name) and priority (allows to specify the zero-based
index in the list of elements to insert the element to). If the priority flag is not
specified, the element will be inserted at the end of the list of the form model's elements.
Below, we provide two code examples illustrating the possible ways of adding elements to a form.
7.8.2. Method 1: Passing an Instance of an Element
The following code fragment creates an instance of the Zend\Form\Element\Text class
and adds the element to the form model:
<?php
namespace Application\Form;
// Define an alias for the class name
use Zend\Form\Form;
use Zend\Form\Element\Text;
// A feedback form model
class ContactForm extends Form
{
// Constructor.
public function __construct()
{
// Create the form fields here ...
$element = new Text(
'subject', // Name of the element
[ // Array of options
'label'=> 'Subject' // Text label
]);
$element->setAttribute('id', 'subject');
// Add the "subject" field to the form
$this->add($element);
}
}
In the code above, we've created an instance of the Zend\Form\Element\Text class (line 15). The
class constructor takes two parameters: the element's name ("subject") and an array of options
(here we specify the text label "Subject").
Additionally, you may configure the element using the methods provided by the Element base class.
For example, in line 20, we set the "id" attribute with the setAttribute() method. For your reference,
the (most important) methods of the Element base class which can be used for
configuring a form element are presented in table 7.9.
| Method name | Description |
|---|---|
setName($name) |
Sets element's name. |
getName() |
Retrieves element's name. |
setOptions($options) |
Sets options. |
getOptions($options) |
Retrieves options. |
getOption($option) |
Retrieves the given option. |
setAttribute($key, $value) |
Sets a single element attribute. |
getAttribute($key) |
Retrieves a single element attribute. |
removeAttribute($key) |
Removes an attribute. |
hasAttribute($key) |
Checks whether such an attribute presents. |
setAttributes($arrayOrTraversable) |
Sets a group of attributes. |
getAttributes() |
Retrieves all attributes at once. |
clearAttributes() |
Removes all attributes at once. |
setValue() |
Sets the element value. |
getValue() |
Retrieves the element value. |
setLabel() |
Sets the label used for this element. |
getLabel() |
Retrieves the label string used for this element. |
setLabelAttributes() |
Sets the attributes to use with the label. |
getLabelAttributes() |
Gets the attributes to use with the label. |
setLabelOptions() |
Sets label specific options. |
getLabelOptions() |
Retrieves label specific options. |
7.8.3. Method 2: Using Array Specification
The second example below (equivalent to the first one) shows how to use an array specification to add an element to form. This method is preferable, because it requires less code to write.
When using array specification for adding an element to a form, the element will be instantiated and configured automatically. Internally, this is accomplished with the help of the
Zend\Form\Factoryfactory class (illustrated by figure 7.13).
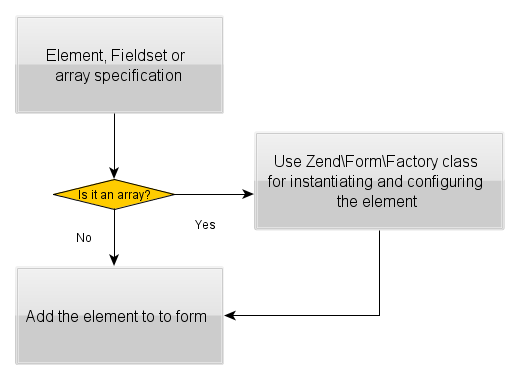 Figure 7.13. The logic of the add() method
Figure 7.13. The logic of the add() method
<?php
namespace Application\Form;
// Define an alias for the class name
use Zend\Form\Form;
// A feedback form model
class ContactForm extends Form
{
// Constructor.
public function __construct()
{
// Add "subject" field
$this->add([
'type' => 'text', // Element type
'name' => 'subject', // Field name
'attributes' => [ // Array of attributes
'id' => 'subject',
],
'options' => [ // Array of options
'label' => 'Subject', // Text label
],
]);
}
}
In line 14 above, we call the form model's add() method to add the element to form.
We pass the element specification to the add() method in the form of an array. The array
has the following typical keys:
the
typekey (line 15) defines the class name to use for instantiation of the element. Here you can use either the fully qualified class name (e.g.Text::class) or its short alias 21 (e.g. "text").the
namekey (line 16) defines the name for the field ("subject").the
attributeskey (line 17) defines the list of HTML attributes to set (here we set the "id" attribute).the
optionsarray (line 18) allows you to specify the text label for the element.
21) If you are confused where we take element aliases from, than you should
know that they are defined inside of the Zend\Form\FormElementManager\FormElementManagerTrait class.



